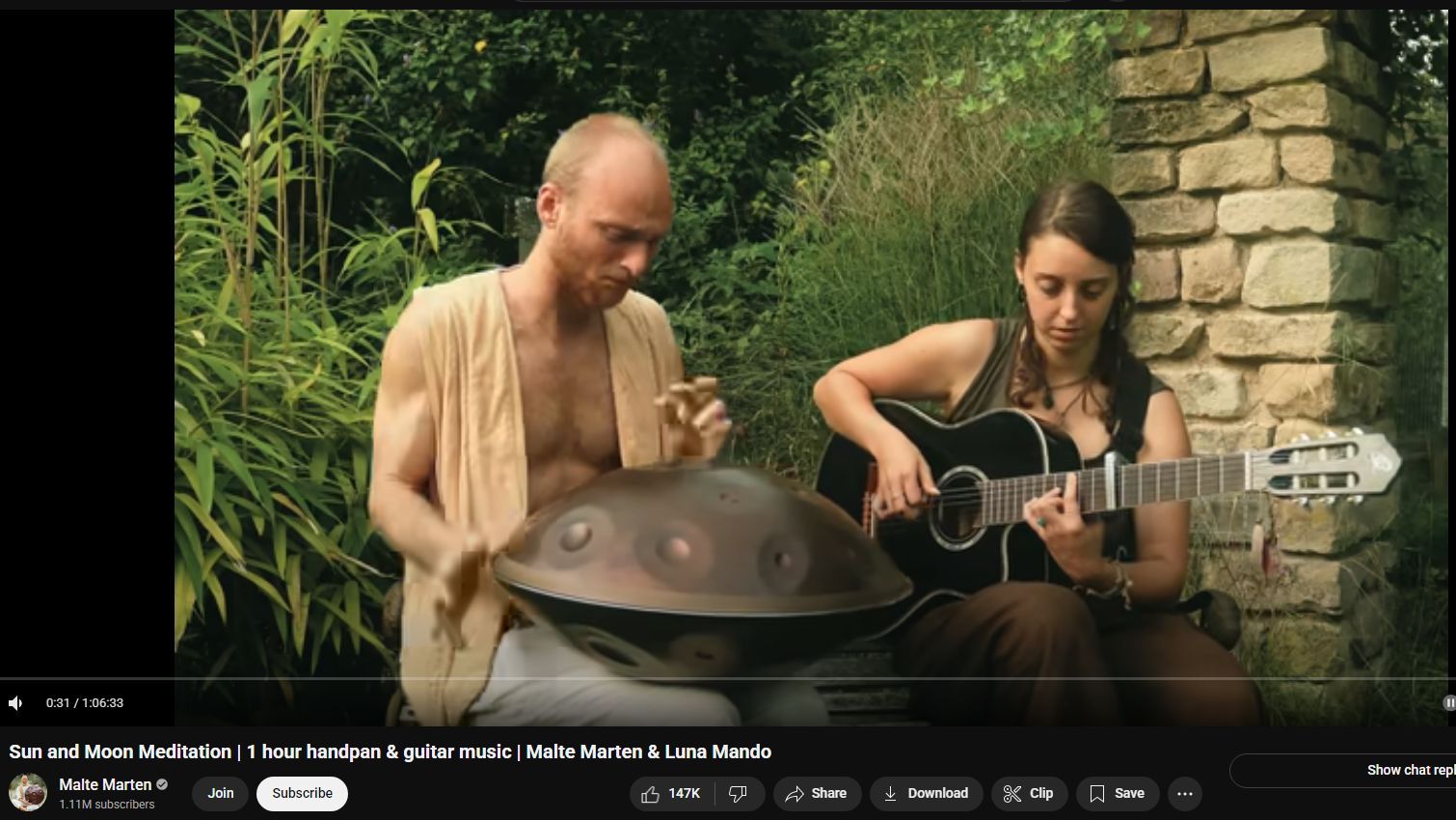
If you’re not smiling at this you may be not right
777 Hz tuned handpan duet.
https://www.bitchute.com/video/46H80iwLalRs

https://www.youtube.com/results?search_query=handpan
No language is more magical than musicians looking at each other and expressing emotions, it is the language that all speak
If dreams had a soundtrack, this would be it.

Handpans are often also called:
- Hang drums (original trademarked name by PANArt, the original Swiss inventors)
- Pantam (a more generic term used by makers to avoid legal issues with “Hang”)
- Handpan drums (most common generic name today)
They are UFO-shaped, convex steel instruments that resemble an inverted steel drum and are played with the fingers. The central dome (called the ding) resonates with deep tones, while the surrounding tone fields produce melodic notes.
Related instruments:
- Tongue drum – often smaller, flat, and with cut slits instead of hammered tone fields
- Steel tongue drum – hybrid between handpan and slit drum
Handpan / Hang Drum: History, Makers, and Traditional Roots
ORIGINS & HISTORY
- 2000 – PANArt invents the Hang
The handpan was first developed in 2000 by PANArt, a Swiss company founded by Felix Rohner and Sabina Schärer. They previously worked on steelpans (Trinidadian steel drums) and applied their knowledge to create the Hang® (pronounced “hahng”), a new idiophone with tuned tone fields on a convex metal shell. - Inspired by multiple traditions
The Hang combines features from: - Steelpan (Trinidad & Tobago)
- Ghatam (South Indian clay pot drum)
- Udu (West African clay drum)
- Gamelan gongs (Indonesia)
- Tabla and frame drums
- Proprietary and limited
PANArt restricted Hang production, releasing only a few hundred per year to handpicked players. This exclusivity created high demand and led to a wave of independent handpan makers globally.
MODERN MAKERS & VARIANTS
After PANArt ceased production of the original Hang, others developed similar instruments under new names (to avoid legal issues):
- Halo – by Pantheon Steel (USA)
One of the earliest alternatives to the Hang, well respected. - SPB (Sculpture), Ayasa, Yishama, Tacta, Echo Sound Sculpture – Europe & Israel
Known for refined craftsmanship, clear tone fields, and custom scale options. - NovaPans, Symphonic Steel, Isthmus Instruments – USA
Affordable models for beginners and intermediate players. - Rav Vast – Russia
A steel tongue drum with a similar UFO shape, using cut slits instead of hammered tone fields. Often mistaken for handpans.
TRADITIONAL ROOTS
While the handpan is a modern invention, its sound and playing technique draw from:
- Gongs and metallophones – Especially from Southeast Asian Gamelan ensembles.
- Frame drums and tabla – Rhythmic finger-drum traditions of India and the Middle East.
- African Udu & Ghatam – Air-based clay percussion instruments that emphasize tonality and breath.
SCALE TYPES & STYLES
- Most handpans are diatonic, centered around a root note and scale (e.g., D Celtic, C Aeolian, Kurd).
- Each handpan is tuned to one fixed scale; there are no frets or retuning options.
- Players focus on meditative, harmonic, or trance-like rhythmic loops.
Here are tuning charts and explanations for handpans (aka Hang drums, pantams). Each handpan is custom-tuned to a fixed scale, generally with 1 central “ding” (bass note) and 7–9 surrounding tone fields.
🥁 STANDARD HANDPAN LAYOUT
A typical 9-note handpan is tuned like this:
Top (Ding) Shell — viewed from above
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
[Note 3] [Note 4] [Note 5]
[Note 2] [Note 6]
[Ding (Root)]
[Note 1] [Note 7]
[Note 8] [Note 9] [Optional]
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––The Ding (center) is the root note of the scale, e.g., D3.
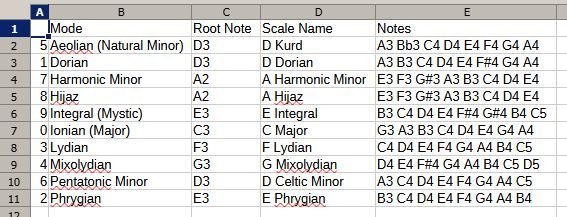
🎼 EXAMPLE SCALES & TUNING CHARTS
1. D Celtic Minor (D Kurd Variant)
Very popular, meditative, melancholic.
Ding: D3
Notes: A3 C4 D4 E4 F4 G4 A4 C5
Scale: D - minor pentatonic with added 6th2. D Kurd (Natural Minor)
Rich and versatile minor mode.
Ding: D3
Notes: A3 Bb3 C4 D4 E4 F4 G4 A4
Scale: D - natural minor (D E F G A Bb C)3. C Major / Ionian
Bright and uplifting.
Ding: C3
Notes: G3 A3 B3 C4 D4 E4 G4 A4
Scale: C - major (C D E F G A B)4. A Hijaz (Middle Eastern / Flamenco)
Exotic, dramatic.
Ding: A2
Notes: E3 F3 G#3 A3 B3 C4 D4 E4
Scale: A - Hijaz (A B C D E F G#)5. E Integral (Zen / Mystic)
Soothing, harmonious, common in Rav Vast and similar.
Ding: E3
Notes: B3 C4 D4 E4 F#4 G#4 B4 C5
Scale: E - Integral / mystical pentatonic🔧 TUNING RANGES
- Ding (center): usually D3–F3
- Tone fields: cover 1–2 octaves above ding (e.g., A3–C5)
- Number of notes: 8 to 21 depending on shell size (9 is most common)
- Frequency accuracy: tuned within ±5 cents of target pitch