From the video comments:
“Maybe another purpose is to sterilize the population by poisoning the public water supplies, as called for in chapter 14 of ECOSCIENCE the 1,400 page textbook by Obama’s science czar. Talk about shedding of microplastics right in to the water, feminizing the men, sterilizing them. Think about it.”
“…”High-density polyethylene (HDPE) is generally considered to be a relatively low shedding material compared to other types of plastics. However, like all plastics, HDPE can release microplastics under certain conditions, especially when it undergoes mechanical abrasion, degradation due to UV exposure, or breaks down over time.” 96 million balls rubbing against each other in the wind and water movements, under intense california sun. Sounds like PERFECT microplastic-creating situation to me, regardless of what type of plastic. So, as I posted, is there a depopulative purpose to placing these endocrine-disrupting toxins right into the worst imaginable situation? Read ECOSCIENCE chapter 14 to learn about the scheme to sterilize the population by poisoning public water supplies. zombietime website has a great write-up on ECOSCIENCE and its co-author Obama science czar John Holdren.”
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uxPdPpi5W4o
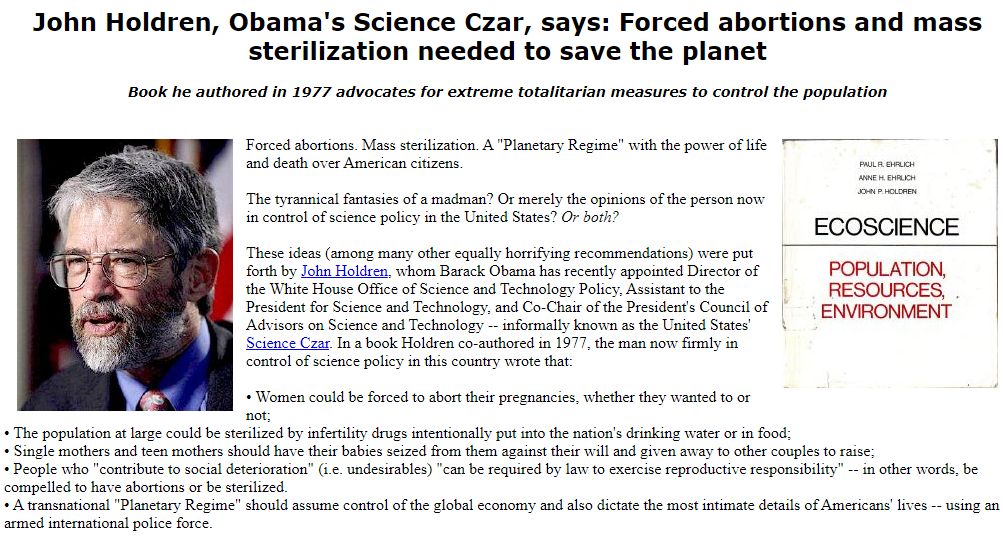
John Holdren’s ECOSCIENCE, a 1,400-page textbook with chapter 14 all about ways to depopulate by secretly sterilizing the human population by poisoning public water supplies —
https://zombietime.com/john_holdren/
PDF – zombietime.com BAD VIBRATIONS
===