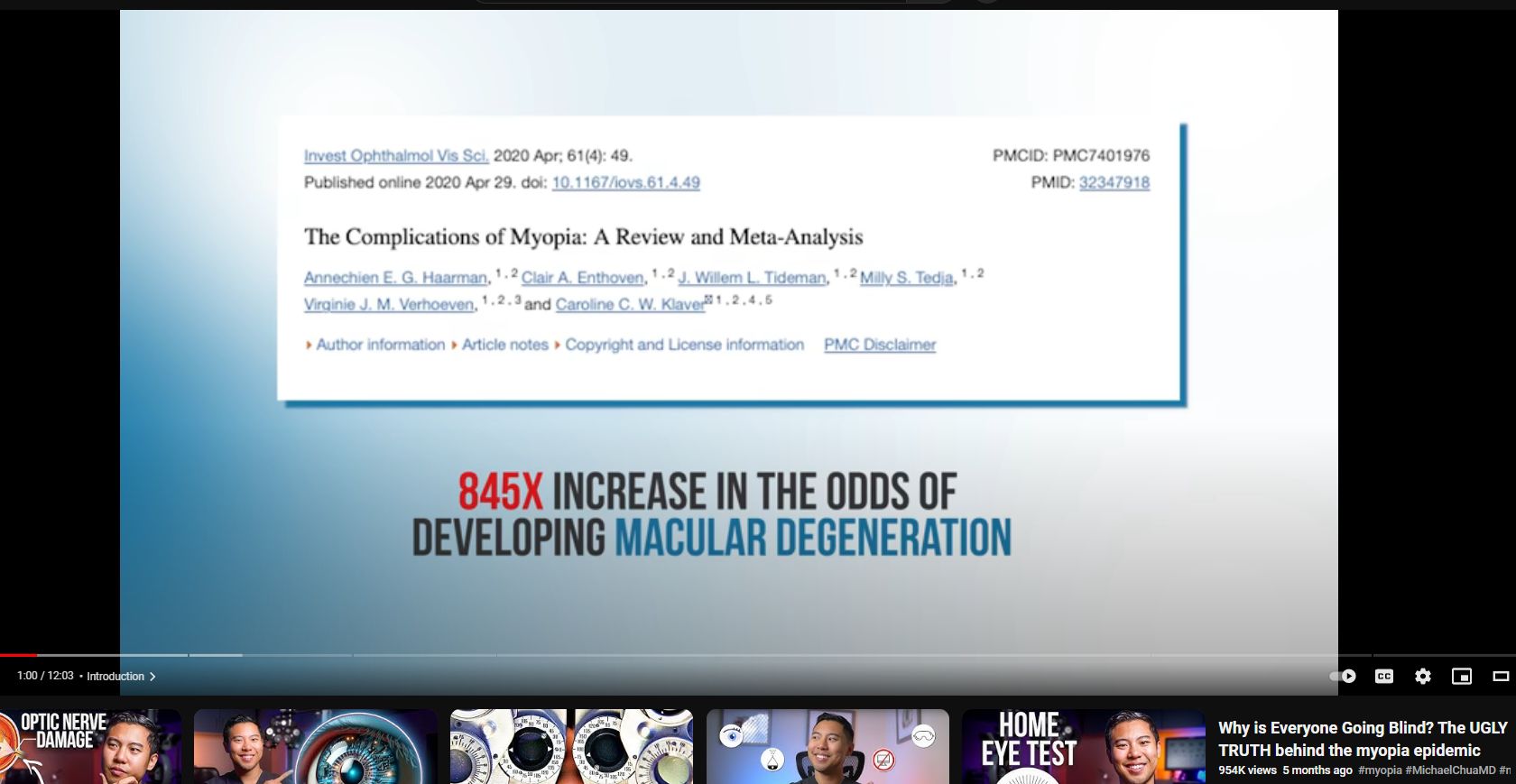
Macular degeneration. Microwave radiation from wifi, cellphones is the largest environmental contaminant that the cell companies never want you to realize is the true culprit.
The effects of microwave radiation on eye health, particularly its potential role in causing macular degeneration and cataracts, are areas of ongoing research and debate. Here’s a detailed explanation of these effects based on current scientific understanding:
1. **Microwave Radiation and Eye Exposure**:
Microwave radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelengths ranging from about one millimeter to one meter. It is commonly produced by microwave ovens, cell phones, Wi-Fi devices, and certain industrial processes. When the eyes are exposed to microwave radiation, several potential effects on eye tissues can occur.
2. **Heat Generation**:
One primary effect of microwave radiation on tissues is the generation of heat. This heat can cause thermal damage to the eye’s structures if the exposure is intense or prolonged. The cornea, lens, and retina are particularly vulnerable to thermal damage, which can contribute to various eye conditions.
3. **Macular Degeneration**:
Macular degeneration is a leading cause of vision loss, especially in older adults. It affects the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp, central vision. While the direct causal link between microwave radiation and macular degeneration is not firmly established, some studies suggest that chronic exposure to high levels of microwave radiation may contribute to retinal damage, including changes in the macula. This damage can lead to the development or progression of macular degeneration over time.
4. **Cataracts**:
Cataracts are another common eye condition characterized by the clouding of the eye’s lens, leading to blurry vision and eventual vision loss if untreated. Microwave radiation, particularly at high levels, has been implicated in the development of cataracts. The mechanism involves the generation of heat in the lens, which can denature proteins and lead to the formation of cataracts over time. However, the threshold levels and duration of exposure required to cause significant cataract formation are not well-defined and may vary among individuals.
5. **Non-Thermal Effects**:
Apart from thermal effects, there is ongoing research into potential non-thermal effects of microwave radiation on eye tissues. These effects may involve oxidative stress, DNA damage, and disruption of cellular signaling pathways. While some studies suggest possible links between non-thermal microwave exposure and eye damage, the exact mechanisms and clinical implications remain areas of active investigation and debate.
6. **Protective Measures**:
To minimize potential risks from microwave radiation exposure to the eyes, individuals can take several protective measures:
– Use microwave ovens and other devices according to safety guidelines and maintain a safe distance during operation.
– Limit prolonged and close-range exposure to microwave-emitting devices.
– Wear appropriate eye protection, such as specialized goggles or glasses, in occupational settings with significant microwave radiation hazards.
– Follow recommended safety practices in industries where microwave equipment is used extensively.
Overall, while there is evidence suggesting a possible link between microwave radiation and eye conditions like macular degeneration and cataracts, further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms and establish clear cause-and-effect relationships. Adhering to safety guidelines and minimizing unnecessary exposure to microwave radiation can help reduce potential risks to eye health.