Do Water Filters Really Purify Your Water

Singapore’s tap water is internally recognized as one of the purest in the world.
See also studies by Dr Emoto and Dr Gerald Pollock (“EZ Water”).
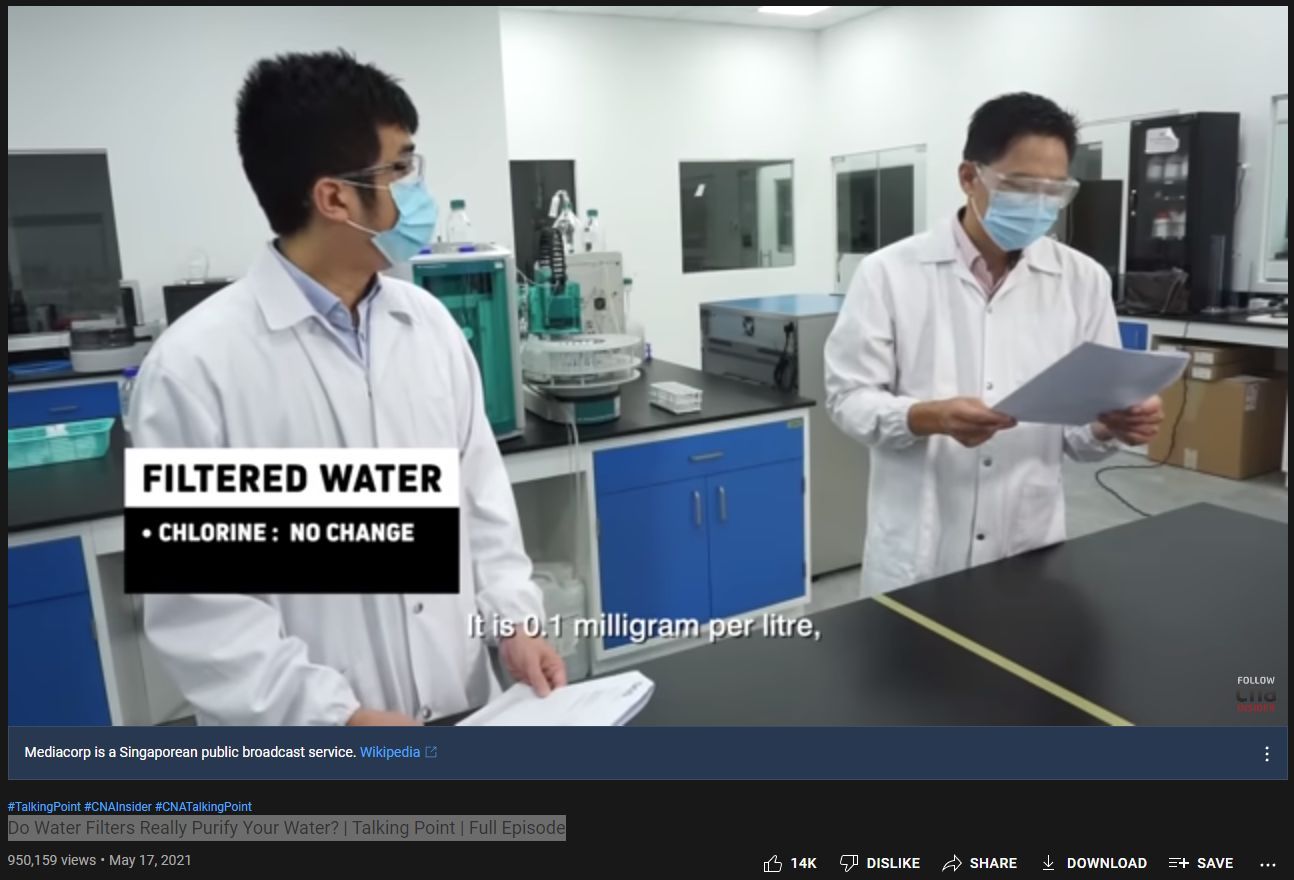
Water test lab revealed:
Chlorine contamination remained unchanged.
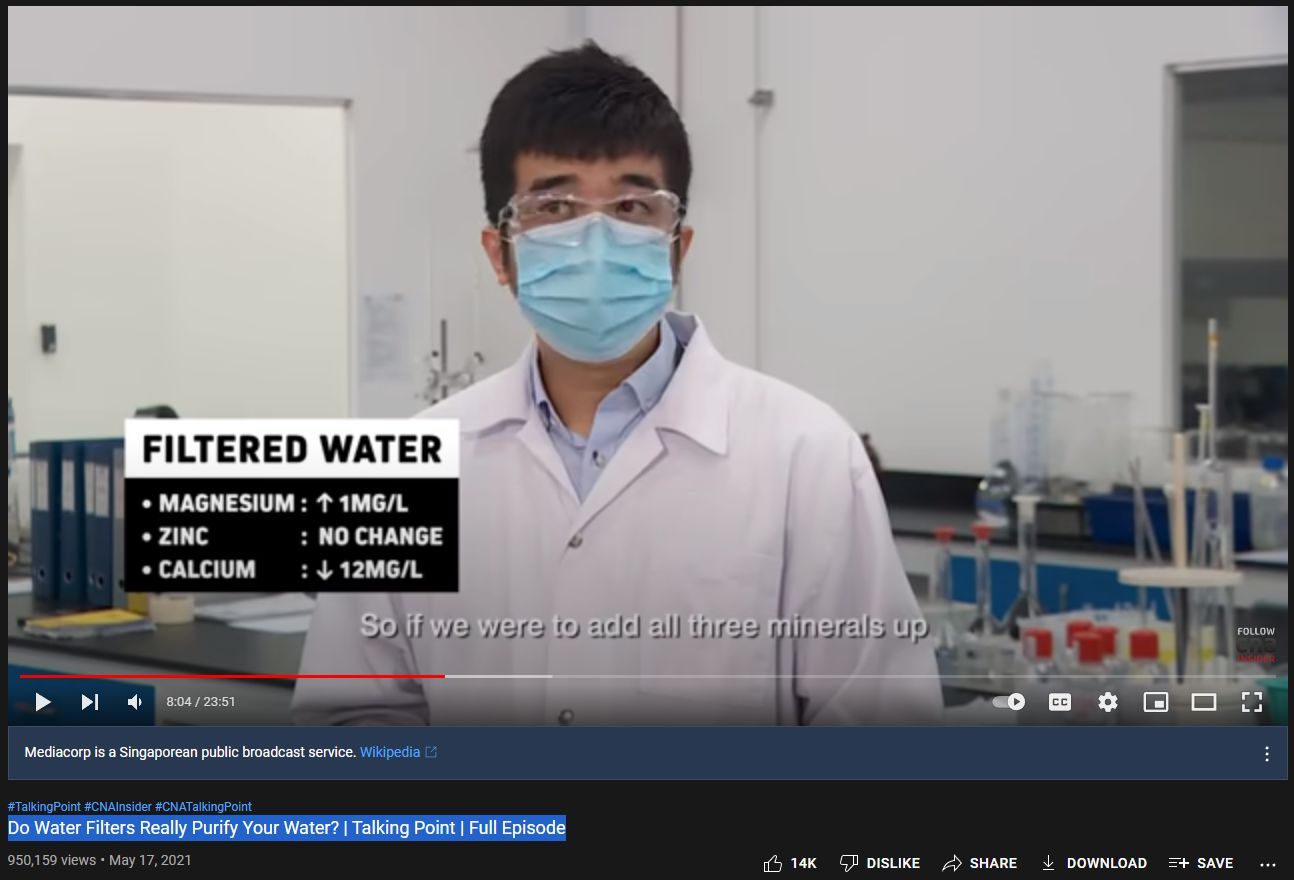
Fluoride contamination decreased from 0.5 mg/l to 0.1 mg/l.
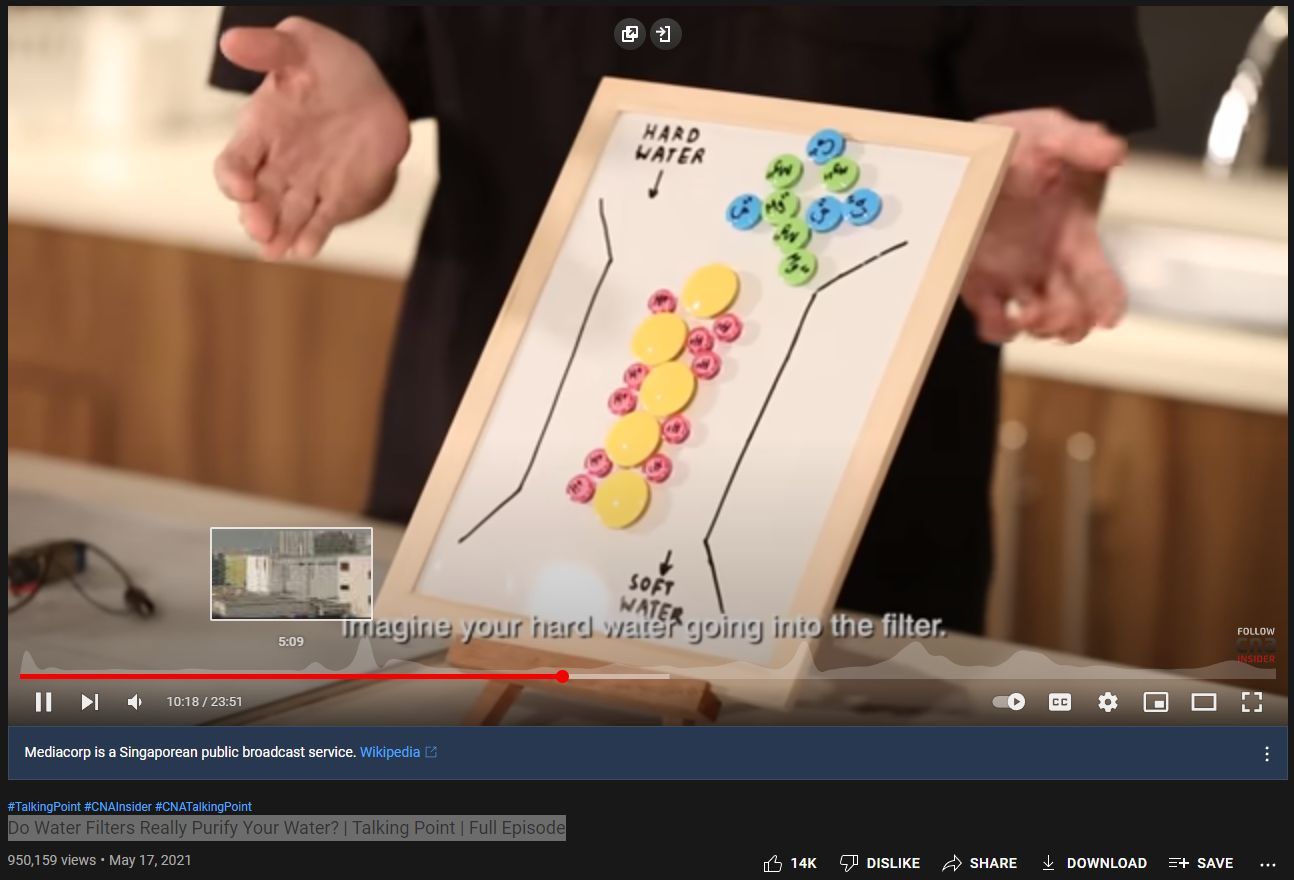
We call milligrams (a weight), “PPM” parts-per-million (also a weight), per unit volume water (usually 1 liter, and 1 liter by definition of PPM).
Remineralization is a lie.
See the blog “Water Quality in Signapore”
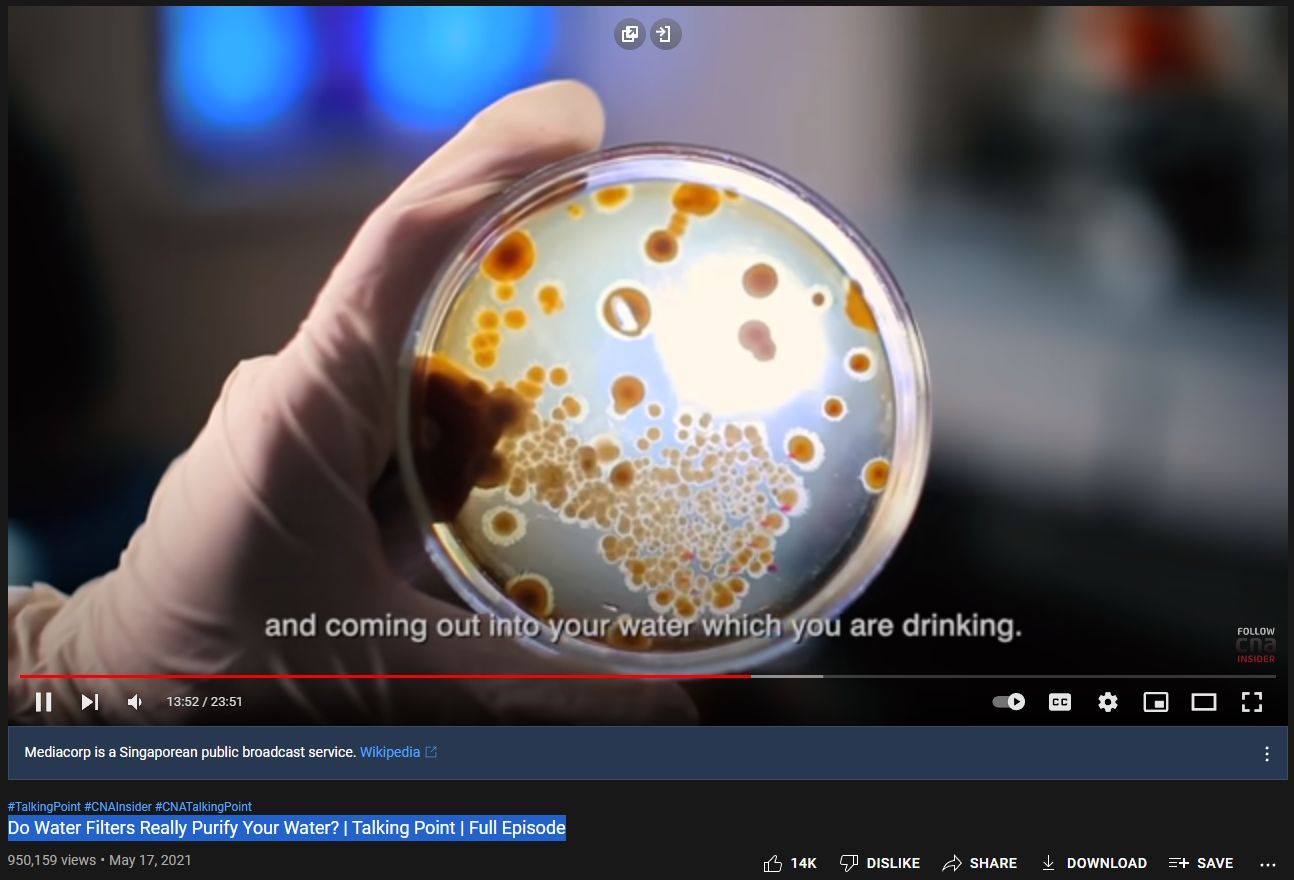
Activated carbon filters absorb organic materials and can begin to host or even grow (fester) poisons.

Water filters are designed to remove impurities and contaminants from water, but the degree to which they purify water depends on the type of filter and its effectiveness. Here’s a breakdown of how water filters work and their ability to purify water:
1. Mechanical Filtration: Many water filters use physical barriers, such as screens, membranes, or porous materials, to trap particles and sediment from water. These filters can effectively remove larger particles, such as dirt, sand, rust, and debris, but may not capture smaller contaminants like bacteria, viruses, and dissolved minerals.
2. Activated Carbon Filtration: Activated carbon filters are commonly used to remove organic compounds, chemicals, and odors from water. The porous structure of activated carbon absorbs and traps contaminants, including chlorine, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), pesticides, and herbicides. However, activated carbon filters may not be effective against heavy metals, minerals, or microbial contaminants.
3. Reverse Osmosis (RO): Reverse osmosis is a filtration process that uses a semipermeable membrane to remove a wide range of impurities from water, including dissolved solids, heavy metals, bacteria, viruses, and other contaminants. RO systems can produce high-quality, purified water, but they may also remove beneficial minerals, require regular maintenance, and produce wastewater.
4. Ultraviolet (UV) Sterilization: UV water purifiers use ultraviolet light to disinfect water by destroying the DNA of microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, and protozoa. UV sterilization is highly effective at killing harmful pathogens but does not remove particulate matter or chemical contaminants. UV systems are often used in combination with other filtration methods for comprehensive water purification.
5. Ion Exchange: Ion exchange filters remove dissolved ions, such as calcium, magnesium, lead, and other heavy metals, from water by exchanging them with ions of similar charge in the filter medium. These filters are commonly used in water softeners to reduce hardness and prevent scale buildup, but they may not remove all contaminants.
In summary, water filters can effectively purify water by removing various impurities and contaminants, depending on the type of filter and its design. It’s essential to choose a water filter that meets your specific needs and addresses the contaminants present in your water supply. Regular maintenance and proper filter replacement are also important for ensuring the continued effectiveness of water filtration systems. Additionally, independent testing and certification by organizations such as NSF International can help verify the performance and reliability of water filters.