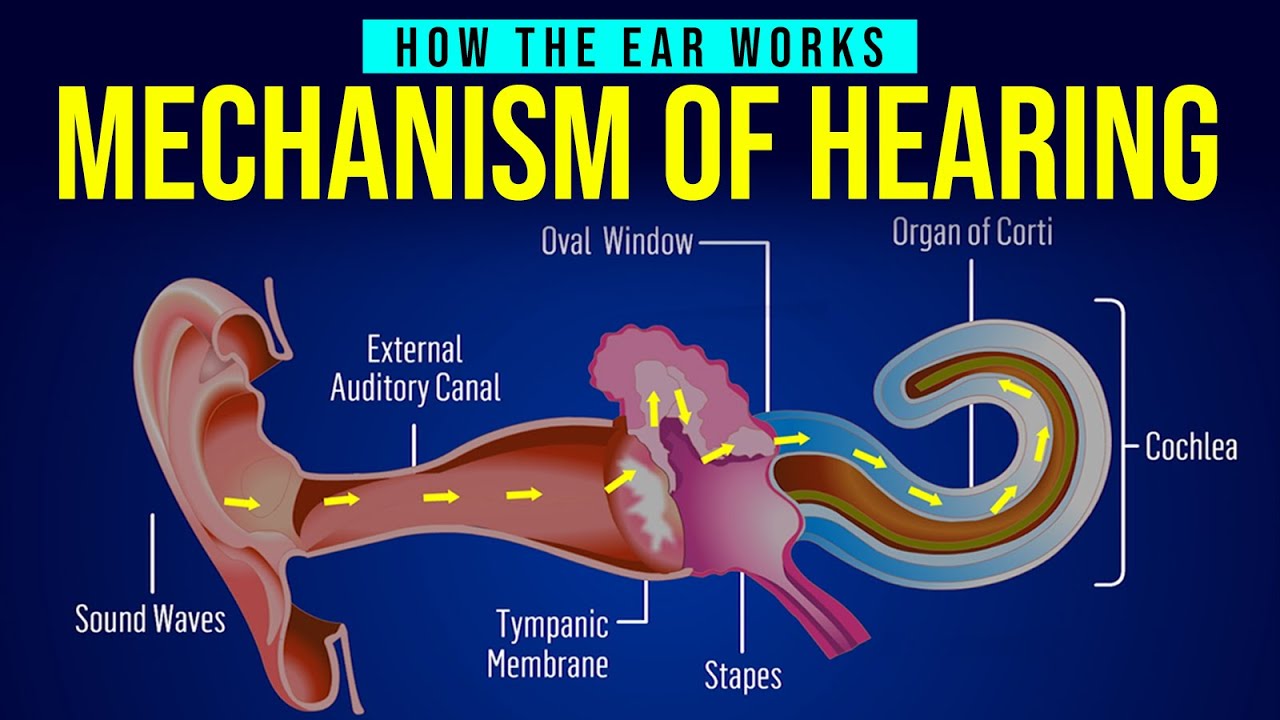
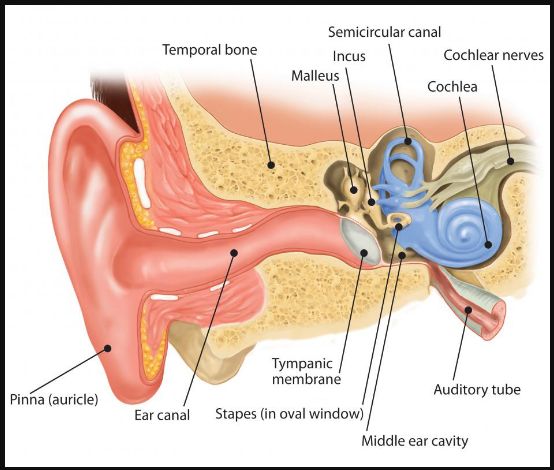
How the human ear works: Science of hearing for musicians
In this video I go over the basics of how a human ear works, and why we all hear things a little differently. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LrM3K8QCJcE === Understanding how the human ear works is crucial for musicians, as it directly affects how they perceive and interact with sound. Here’s a simplified overview of the science of … Read more